It felt like spring and summer arrived at the same time this year and as if the changes in atmospheric pressure, also transpired into severe industry pressures to get projects completed before the end of the year. When the pressure is on, it's easy to default to old habits while small adjustments could actually speedup what you need to do. With this single purpose in mind, SIMTEQ hosted a technology day in Stellenbosch to bring our customers up to speed and invited two companies to share their challenges and successes with the audience. De Beers Marine shared how they applied Adams in a successful redesign of a Nutator to prevent costly durability failures and Dragonfly Aerospace shared their unique experience having their first satellite launched successfully with Space-X from Florida into orbit. This month is also time for the quarterly new product releases and we share the latest additions in this newsletter.
Don't miss the new improvements and work smarter, not harder!








Our latest newsletter feature takes inspiration from the educational and visually engaging 'Deep Learning' series by 3Blue1Brown. In this chapter, we delve into the heart of neural networks, exploring the captivating concept of gradient descent and how it drives the learning process. Join us as we unravel the 'Art of Engineering' behind neural networks, gaining insights from this insightful video by 3Blue1Brown. Get ready to enhance your understanding of neural networks and machine learning through the lens of one of the most renowned educational channels on YouTube, and if you don't want to implement this yourself, use Odyssee CAE which packaged Machine Learning for you.
CAEfatigue 2023.1.1 is now available at the Software Download Center. This patch release addresses several user reported bugs that were found in the previous release, including: Solver related:
User Interface related:
We recommend upgrading to this version. As a further reminder, some main highlights recently introduced with 2023.1 included
Click here to learn about What’s New in CAEfatigue 2023.1.1. |
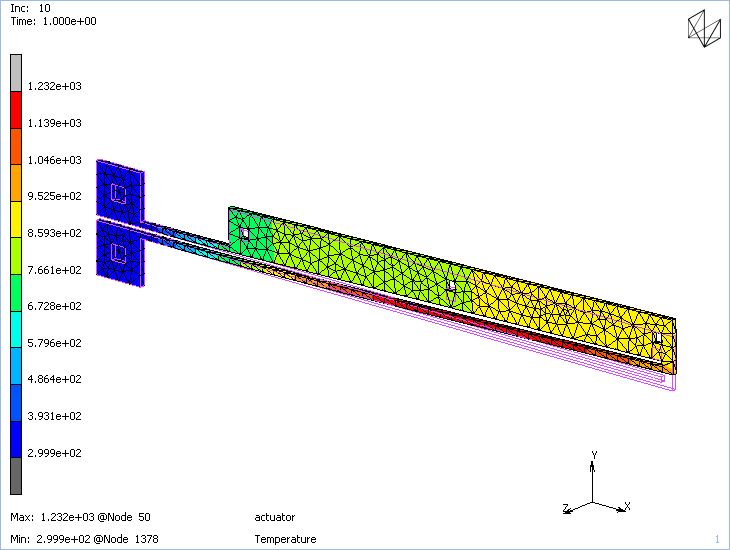
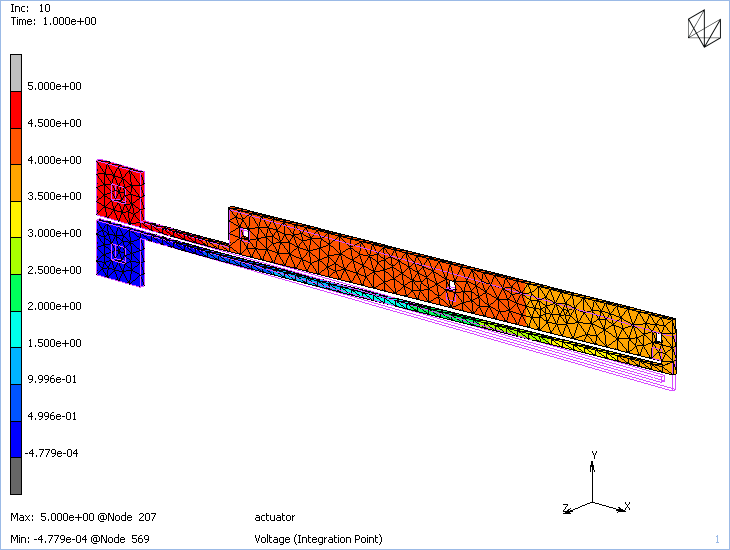
Dytran 2023.1 is now available at the Software Download Center. Click here to learn about What’s New in Dytran 2023.1. Some main highlights of this release include:
|
Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence is pleased to announce the launch of Easy5 2023.2. There are some changes that require your attention and some new features that may interest you: Runtime Licensing for Easy5 Analyses has been restored to the Easy5 2010 state:
Also, during the process of exporting an FMU, a standalone single-call analysis of the model being exported is performed. Hence, the above RT license feature prerequisites are also required (briefly) during the process of FMU Export- the EASY5_RT_Analysis feature for all models and the appropriate library RT license features listed above if the model being exported contains GD, HC, HB or VC library components. What's New in Easy5 2023.2 External Heat Transfer to Thermal Hydraulics Pipe Walls A new component IN, Pipe Insulation and Heat Transfer to Ambient, has been added. This component makes ported connections to pipe walls and can be used to model heat transfer in the environment. Coming Soon… Updates have been made to Easy5 to support authoring of Easy5 models from the UI of Elements 2023.2. A user will be able to access Easy5 libraries to create an Easy5 model as a sub-system inside an Elements model. Easy5 2023.2 is now available at the Software Download Center. Click here to learn about What’s New in Easy5 2023.2. |
FormingSuite 2023.3 is now available at the Software Download Center. Click here to learn about What’s New in FormingSuite 2023.3. Some of the FTI FormingSuite 2023.3 highlights include the following: Introduced display of minimum deviation
ARC/LS-Dyna file export
Hole creation to intermediate geometry
User Experience Improvements
|

Simufact Additive 2023.3 is now available at the Software Download Center. Look forward to the new highlights of Simufact Additive 2023.3, which include:
Visit the SimCompanion website to discover all the great new enhancements in Simufact Additive 2023.3. Upgrade to Simufact Additive 2023.3 and benefit from the new features that improve your daily work! |
We are pleased to inform you about the new software release Simufact Forming 2023.3, that is now available at the Software Download Center. Look forward to the new highlights which include:
|

|
Visit the SimCompanion website to discover all the great new enhancements in Simufact Forming 2023.3. Upgrade to Simufact Forming 2023.3 and benefit from the new features that improve your daily work! |
Simufact Welding 2023.3 is now available at the Software Download Center. Click here to learn about What’s New in Simufact Welding 2023.3. Some of the Simufact Welding 2023.3 highlights include the following: Geometry Boundary Conditions
Spot-wise remeshing capabilities for all RSW modes
Enhanced Morphing Tool
New ‘solver pinning’ option
Updated Material Database
Further Improvements
|




Software Package: MSC Apex
Price: R 18 300.00/p excl VAT (A 25% discount applies if attendance is online)
Date: 02 - 06 Oct 2023
Duration: 5 Days
CPD Accredited: Yes
Price: R 7 320.00/p excl VAT (A 25% discount applies if attendance is online)
Date: 17 - 18 Oct 2023
Duration: 2 Days
CPD Accredited: Yes
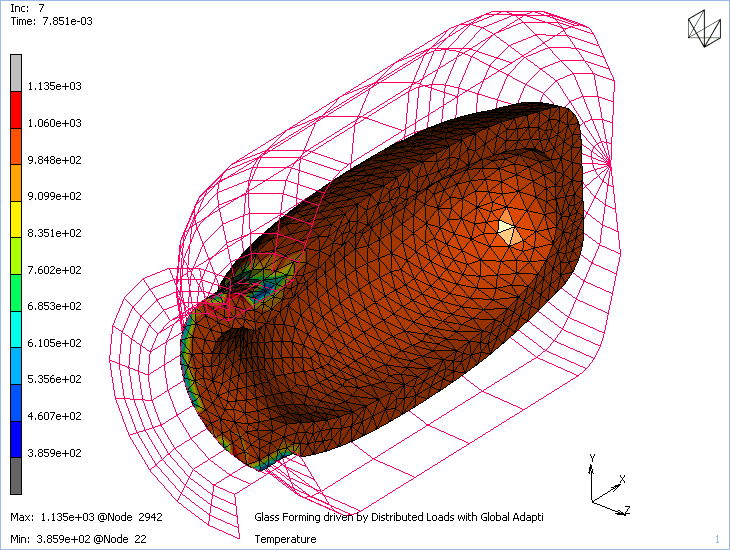
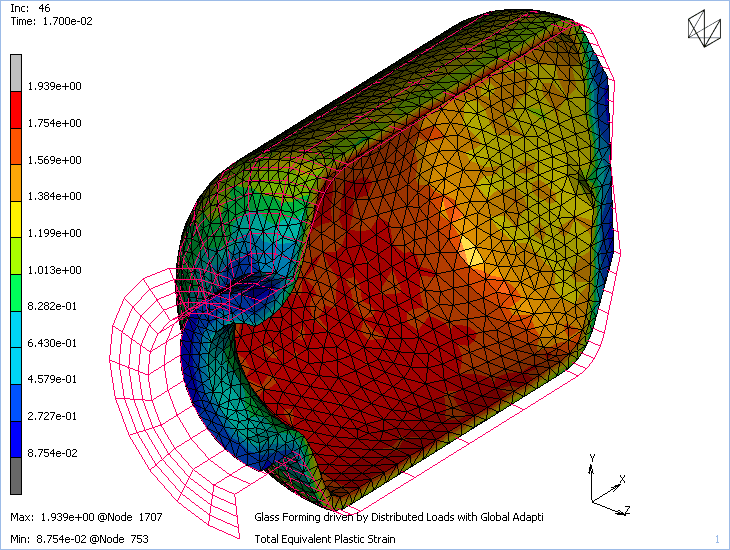
Software Package: Marc
Price: R 18 300.00/p excl VAT (A 25% discount applies if attendance is online)
Date: 13 - 17 Nov 2023
Duration: 5 Days
Price: R 7 320.00/p excl VAT (A 25% discount applies if attendance is online)
Date: 21 - 22 Nov 2023
Duration: 2 Days
CPD Accredited: Yes